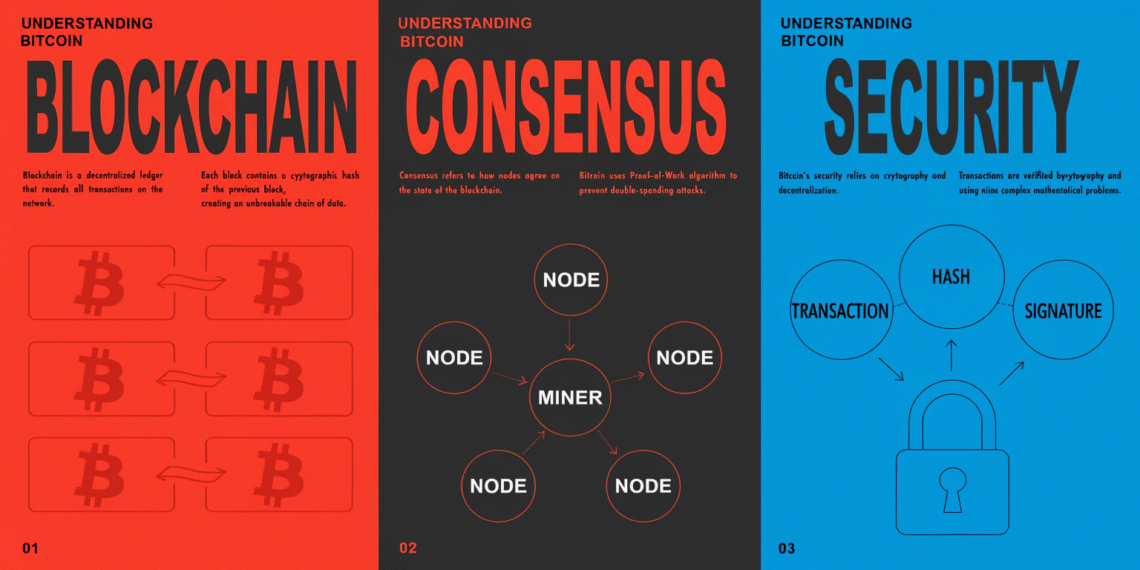
Understanding Bitcoin Technology is more than a digital currency — it’s a technological revolution that relies on blockchain, consensus algorithms, and cryptography to operate securely without intermediaries. For beginners and even experienced investors, understanding the technology behind Bitcoin is essential to appreciate its value and trustworthiness.
From my experience guiding crypto enthusiasts, the core strength of Bitcoin lies in its decentralized network, immutability, and cryptographic security. In 2025, as Bitcoin adoption grows, these technological fundamentals remain the backbone of its success.
In this guide, we’ll break down how Bitcoin’s blockchain works, explain the Proof of Work consensus mechanism, examine its security features, and clarify why Bitcoin continues to be the most secure and trusted cryptocurrency in the world.
What Is the Bitcoin Blockchain?
The Bitcoin blockchain is a public, decentralized ledger that records all transactions securely. Key features:
Decentralized: No central authority controls it
Immutable: Transactions cannot be altered once confirmed
Transparent: Anyone can view transaction history
Pro Tip: Every Bitcoin transaction is recorded in blocks, linked chronologically, forming the blockchain.
How Bitcoin Transactions Work
1. Transaction Initiation
User creates a transaction with sender, receiver, and BTC amount
Transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network
2. Verification by Miners
Miners validate transactions using cryptographic proofs
Verified transactions are grouped into a block
3. Adding Blocks to the Chain
Miners solve a complex mathematical puzzle (Proof of Work)
First miner to solve it adds the block and earns rewards
Block is timestamped and linked to the previous block
Investor Insight: This process ensures all transactions are secure, verified, and tamper-proof.
Proof of Work Consensus Explained
What Is Proof of Work (PoW)?
PoW is the mechanism that secures the Bitcoin network:
Miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles
Requires significant computational power
Ensures network security and prevents double-spending
Why PoW Matters
Makes Bitcoin decentralized and trustless
Prevents malicious actors from altering the blockchain
Rewards miners for securing the network
Mini-case study: Even with rising hash rates in 2025, the PoW system remains resilient against attacks.
Bitcoin Network Security Features
1. Cryptographic Hashing
SHA-256 algorithm secures transactions and blocks
Each block has a unique hash; altering data changes the hash, revealing tampering
2. Decentralization
Thousands of nodes globally verify transactions
No single point of failure or control
3. Immutability
Once a block is added, it cannot be modified
Ensures trust and transparency
4. Incentives for Miners
Block rewards and transaction fees motivate miners to act honestly
Economic incentives prevent malicious attacks
Advantages of Bitcoin Technology
Security: Resistant to hacks and fraud
Transparency: All transactions publicly recorded
Decentralization: No central authority can manipulate the system
Scarcity: Fixed supply of 21 million BTC ensures value over time
Global Accessibility: Anyone with internet can participate
Investor Insight: These features make Bitcoin a secure store of value and digital gold in 2025.
Common Misconceptions
Bitcoin is anonymous: It’s pseudonymous; transactions are traceable
PoW wastes energy: Energy secures the network and is increasingly sourced from renewables
Blockchain is slow: Bitcoin prioritizes security over speed; Layer 2 solutions improve scalability
FAQs
Q1: What makes Bitcoin secure?
A: Bitcoin’s security comes from decentralization, cryptography, Proof of Work, and network incentives.
Q2: How does the blockchain work?
A: Transactions are grouped into blocks, verified by miners, and linked in a chronological, immutable chain.
Q3: What is Proof of Work?
A: PoW is a consensus mechanism where miners solve complex puzzles to validate transactions and secure the network.
Q4: Can Bitcoin be hacked?
A: The network itself is extremely secure due to decentralization and cryptographic protections, though individual wallets can be targeted.
Q5: How many Bitcoins will exist?
A: Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins.
Q6: Is Bitcoin truly decentralized?
A: Yes, thousands of nodes worldwide validate transactions without a central authority.
Internal Links
Bitcoin for Beginners: How to Buy, Store & Use BTC in 2025
Bitcoin Wallet Setup Guide: Hot vs Cold Wallets Explained
How to Trade Bitcoin Safely: Tips for Beginners