INTRODUCTION
Consensus mechanisms are the heart of blockchain technology, determining how transactions are verified, blocks are added, and the network remains secure. In 2025, as blockchain adoption expands across industries, understanding PoW, PoS, and alternative mechanisms is crucial for developers, investors, and crypto enthusiasts.
From my experience studying blockchain networks, these mechanisms not only ensure security and decentralization but also influence energy consumption, scalability, and participation incentives.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most widely used consensus mechanisms, explain how they work, compare their advantages and drawbacks, and examine their real-world applications. By the end, you’ll understand which mechanism suits different blockchain networks and why they are critical for trustless systems.
What Are Consensus Mechanisms?
A consensus mechanism is a protocol that allows blockchain nodes to agree on a single version of the truth without relying on a central authority.
Key purposes:
Validate transactions
Secure the network against attacks
Ensure trust among decentralized participants
Investor Insight: Consensus mechanisms are what make decentralized networks trustworthy and resilient against malicious actors.
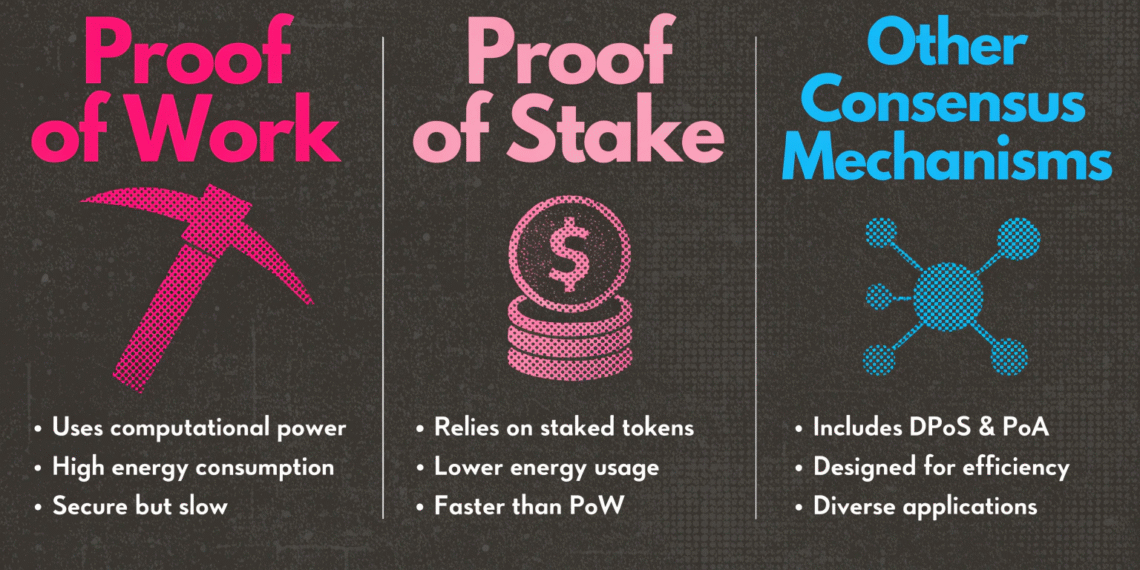
Proof of Work (PoW)
How PoW Works
Miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles
First miner to solve it adds a new block to the blockchain
Rewards are given in the network’s native cryptocurrency
Example: Bitcoin and Litecoin use PoW.
Advantages of PoW
Highly secure due to computational difficulty
Proven and time-tested (Bitcoin has run on PoW since 2009)
Drawbacks of PoW
High energy consumption
Requires expensive hardware (ASICs)
Slower transaction processing compared to PoS
Mini-case study: Bitcoin’s PoW network consumes energy comparable to a small country, sparking debates about sustainability.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
How PoS Works
Validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they stake
Staked coins act as collateral against dishonest behavior
Example: Ethereum 2.0, Cardano
Advantages of PoS
Energy-efficient compared to PoW
Encourages network participation via staking rewards
Faster transaction processing
Drawbacks of PoS
Wealth concentration risk (those with more coins have more influence)
Requires reliable node operation to avoid penalties
Investor Insight: PoS makes blockchain eco-friendly and scalable while maintaining security.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
How DPoS Works
Coin holders vote for delegates to validate transactions
Delegates produce blocks on behalf of the network
Example: EOS, Tron
Advantages of DPoS
Extremely fast transaction processing
Lower energy usage than PoW
Community-driven governance
Drawbacks of DPoS
Centralization risk if few delegates dominate
Vulnerable to collusion among delegates
Other Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Authority (PoA): Trusted validators verify transactions; used in private blockchains
Proof of Burn (PoB): Miners “burn” coins to gain the right to mine
Hybrid Mechanisms: Combine PoW and PoS for security and efficiency
Pro Tip: Different mechanisms suit different networks — PoW for maximum security, PoS for energy efficiency, PoA for enterprise blockchains.
Comparing Consensus Mechanisms
| Mechanism | Security | Energy Efficiency | Decentralization | Speed | Use Case |
| PoW | High | Low | High | Medium | Bitcoin, Litecoin |
| PoS | Medium-High | High | Medium | Fast | Ethereum 2.0, Cardano |
| DPoS | Medium | High | Medium-Low | Very Fast | EOS, Tron |
| PoA | Medium | Very High | Low | Very Fast | Enterprise/Private |
Investor Insight: Understanding the trade-offs helps in choosing networks to invest in or develop on.
Real-World Applications in 2025
Bitcoin: Secure digital gold using PoW
Ethereum 2.0: Decentralized apps with PoS
EOS/Tron: High-speed dApps using DPoS
Private Blockchains: Supply chain, healthcare, and enterprise systems using PoA
Mini-case study: Supply chain networks often use PoA for controlled access, while public finance apps rely on PoS for energy efficiency and scalability.
FAQs (Schema-Ready)
Q1: What is a blockchain consensus mechanism?
A: It’s a protocol that allows all nodes in a network to agree on a single version of the blockchain, ensuring security and trust.
Q2: What is the difference between PoW and PoS?
A: PoW uses computational work to validate blocks, consuming high energy, while PoS uses staked coins and is more energy-efficient.
Q3: What is DPoS?
A: Delegated Proof of Stake allows coin holders to vote for delegates who validate transactions on their behalf.
Q4: Which consensus mechanism is most secure?
A: PoW is highly secure due to computational difficulty, but PoS and DPoS are secure when properly implemented.
Q5: Can private blockchains use these mechanisms?
A: Private blockchains often use PoA or hybrid models optimized for speed and controlled access.
Q6: How do consensus mechanisms affect scalability?
A: Mechanisms like PoS and DPoS are faster and more scalable, while PoW is slower but highly secure.
Internal Links
Blockchain Technology Explained: How It Works & Key Use Cases in 2025
DeFi Explained: Opportunities & Risks in 2025
Web3 & Decentralization: The Future of the Internet
External Links (High Authority)